RACI matrix and examples of its use in project management
In project management, you need to design and change processes while communicating with team members to properly assign roles. The number of processes that need to be controlled makes the work process very complicated. A tool like the RACI matrix can quickly simplify these tasks.
The advantage of the RACI matrix is that it is a convenient way to assign authority and responsibility. There are several variations of the matrix, each with its own characteristics and nuances. However, we will look at the classic version.
What is the RACI matrix? The RACI matrix can be described as a tool that allows each of the project participants to assign a role and tasks that they will perform.
In simple terms, the definition of the RACI matrix is an acronym consisting of concepts that stand for:
- R – Responsible – the person responsible for the work is the direct performer of the task;
- A – Accountable – responsible for the outcome – the one who accepts the work;
- C – Consult before doing – someone who consults during the work;
- I – Inform after doing – informed – someone who is aware of any changes and decisions made in the course of the work.
These terms are used in a table that indicates what task the team member who plays a certain role in the project will perform. Depending on the project, we can distinguish such process roles:
- process owner;
- process manager;
- assistant manager;
- CI category owner.
The types of activities include: adding a new category, providing information, updating information, auditing, process improvement, and others.
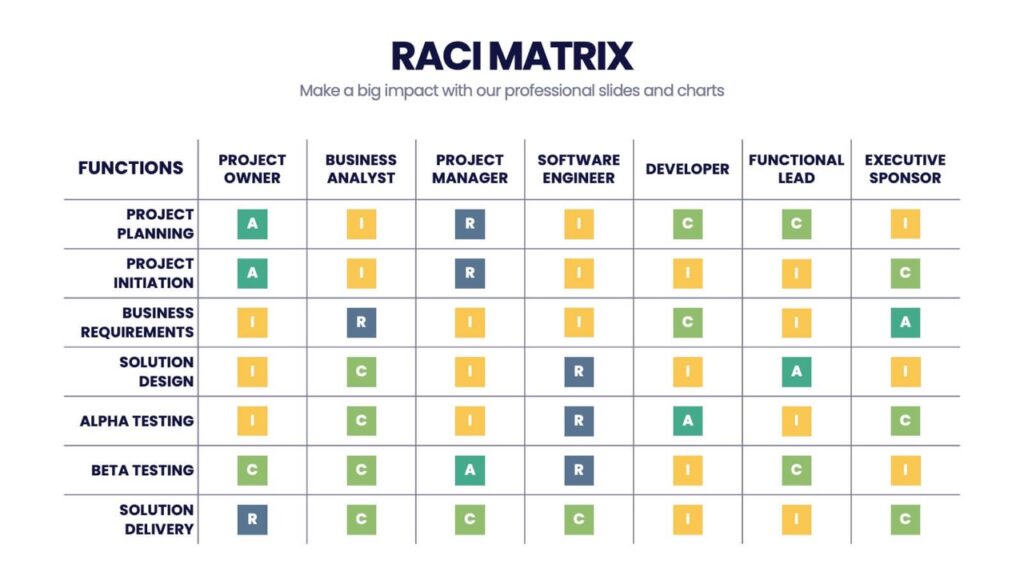
The table assigns each role one of the RACI acronyms values that it must adhere to in the course of a particular task. For example, a process manager must adhere to the RA value when providing information. At the same time, the assistant manager must comply with the R-value when updating information.
There are several important rules of the RACI matrix that should be kept in mind when creating the table. First, there should be only one accountable person. Sometimes it is acceptable to assign two accountable values. But in this case, it is necessary to clearly specify the situations in which each of the roles has its share of responsibility in performing each of the tasks. However, this complicates the creation of the table somewhat, which changes the approach to creating it.
In addition, the Responsible must be in each of the activities, and there can be several of them, and they can be combined. For example, the assistant manager and the CI category owner are both responsible for auditing. And accordingly, in the RACI table, these two roles have the value R for the “audit” activity.
It is also worth noting that each activity must have an Accountable and a Responsible. This means that one or more roles must both do the work and be responsible for the result.
The RACI matrix is a handy tool to help you quickly assign tasks and control the work process. Roles and tasks may change from project to project, but the principle of the matrix remains the same.




